
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
 Figure 1 -
Total solar radiation at the top of the atmosphere. Smithsonian Meteorological Tables,
1968.
Figure 1 -
Total solar radiation at the top of the atmosphere. Smithsonian Meteorological Tables,
1968.
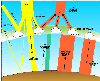 Figure 2 -
Solar and terrestrial radiation balance. (CALMET '95, AL Working
group of SCHOTI.)
Figure 2 -
Solar and terrestrial radiation balance. (CALMET '95, AL Working
group of SCHOTI.)
 Figure 3 - Albedos for the shortwave
portion of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Figure 3 - Albedos for the shortwave
portion of the electromagnetic spectrum.
 Figure 4 - Absorption
spectra for major natural greenhouse gases in the earth's atmosphere. (After J. N. Howard, 1959:
Proc. I.R.E. 47, 1459; and R. M. Goody and G.D. Robinson, 1951: Quart. H. Roy.
Meteorol. Soc. 77, (153)
Figure 4 - Absorption
spectra for major natural greenhouse gases in the earth's atmosphere. (After J. N. Howard, 1959:
Proc. I.R.E. 47, 1459; and R. M. Goody and G.D. Robinson, 1951: Quart. H. Roy.
Meteorol. Soc. 77, (153)
 Figure 5 - Expressions used to derive
radiative forcing for past trends and future scenarios of greenhouse gas
concentrations. Adapted from Houghton, J.T., G.J. Jenkins,
J.J. Ephraums, eds, 1990: 1990 Intergovernment Panel on Climate Change, Cambridge University
Press.
Figure 5 - Expressions used to derive
radiative forcing for past trends and future scenarios of greenhouse gas
concentrations. Adapted from Houghton, J.T., G.J. Jenkins,
J.J. Ephraums, eds, 1990: 1990 Intergovernment Panel on Climate Change, Cambridge University
Press.
 Figure 6 - Radiative forcing relative
to CO2 per unit molecule change. Adapted from
Houghton, J.T., G.J. Jenkins, J.J. Ephraums, eds, 1990: 1990
Intergovernment Panel on Climate Change, Cambridge University
Press.
Figure 6 - Radiative forcing relative
to CO2 per unit molecule change. Adapted from
Houghton, J.T., G.J. Jenkins, J.J. Ephraums, eds, 1990: 1990
Intergovernment Panel on Climate Change, Cambridge University
Press.
 Figure 7 - Radiative forcing
of a number of CFCs. Adapted from Houghton, J.T., G.J. Jenkins, J.J. Ephraums, eds, 1990: 1990
Intergovernment Panel on Climate Change, Cambridge University
Press.
Figure 7 - Radiative forcing
of a number of CFCs. Adapted from Houghton, J.T., G.J. Jenkins, J.J. Ephraums, eds, 1990: 1990
Intergovernment Panel on Climate Change, Cambridge University
Press.
 Figure 8 - Decadal contributions to radiative
forcing due to increases in greenhouse gas concentrations for periods between
1765 and 1990. Houghton, J.T., G.J. Jenkins,
J.J. Ephraums, eds, 1990: 1990 Intergovernment Panel on Climate Change, Cambridge University
Press.Figure 2.3, page 55.
Figure 8 - Decadal contributions to radiative
forcing due to increases in greenhouse gas concentrations for periods between
1765 and 1990. Houghton, J.T., G.J. Jenkins,
J.J. Ephraums, eds, 1990: 1990 Intergovernment Panel on Climate Change, Cambridge University
Press.Figure 2.3, page 55.
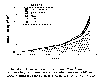 Figure 9 - Changes in radiative forcing due to
increases in greenhouse gas concentrations between 1765 and 1990. Houghton, J.T., G.J. Jenkins,
J.J. Ephraums, eds, 1990: 1990 Intergovernment Panel on Climate Change, Cambridge University
Press.Figure 2.2, page 55.
Figure 9 - Changes in radiative forcing due to
increases in greenhouse gas concentrations between 1765 and 1990. Houghton, J.T., G.J. Jenkins,
J.J. Ephraums, eds, 1990: 1990 Intergovernment Panel on Climate Change, Cambridge University
Press.Figure 2.2, page 55.
 Figure 10 - Comparison
of Enhanced Greenhouse Forcing with other Radiative Influences.
Figure 10 - Comparison
of Enhanced Greenhouse Forcing with other Radiative Influences.
 Figure 11 - Reconstructed solar
irradiance from 1874-1988. Houghton, J.T., G.J. Jenkins, J.J.
Ephraums, eds, 1990: 1990 Intergovernment Panel on Climate Change,
Cambridge University Press.
Figure 11 - Reconstructed solar
irradiance from 1874-1988. Houghton, J.T., G.J. Jenkins, J.J.
Ephraums, eds, 1990: 1990 Intergovernment Panel on Climate Change,
Cambridge University Press.
 Figure 12 - Global warming climate runs with CO2 and sulfate aerosols
(A consortium for the Application of Climate Impact Assessments).
Figure 12 - Global warming climate runs with CO2 and sulfate aerosols
(A consortium for the Application of Climate Impact Assessments).
 Figure 13 - Comparing the global
heating and cooling from fossil fuel combustion. DOE research summary, December, 1993,
CDIAC.
Figure 13 - Comparing the global
heating and cooling from fossil fuel combustion. DOE research summary, December, 1993,
CDIAC.
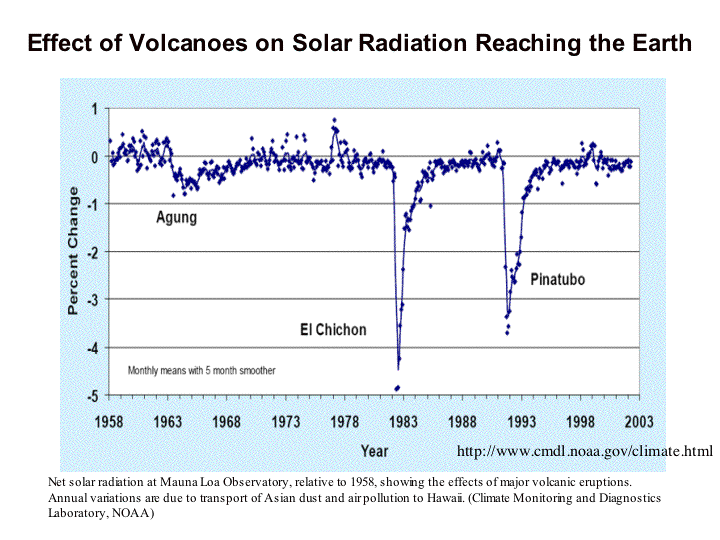 Figure 14 -
Effect of volcanoes on solar radiation reaching the Earth. Climate Monitoring and Diagnostics Laboratory
(NOAA).
Figure 14 -
Effect of volcanoes on solar radiation reaching the Earth. Climate Monitoring and Diagnostics Laboratory
(NOAA).
Related Class Images
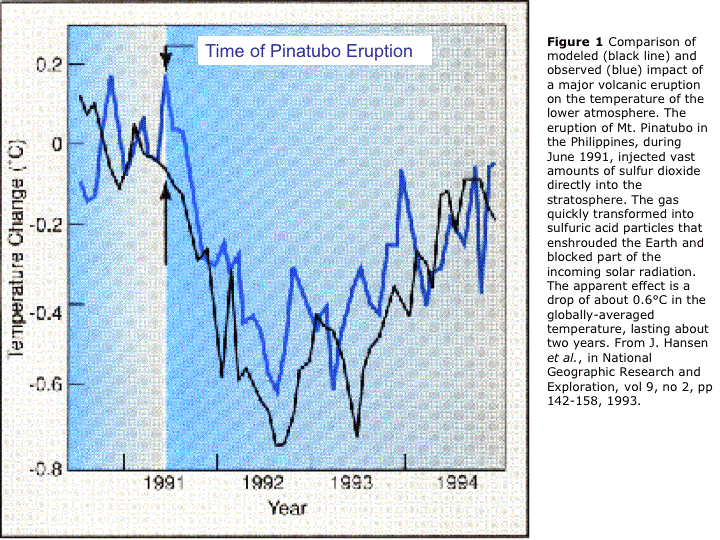 Comparison of modeled and observed lower atmosphere temperature following a
major volcanic eruption. From J. Hansen et al., National Geographic Research and
Exploration, vol 9, no 2, pp 142-158, 1993.
Comparison of modeled and observed lower atmosphere temperature following a
major volcanic eruption. From J. Hansen et al., National Geographic Research and
Exploration, vol 9, no 2, pp 142-158, 1993.
Back to Unit Page